常用配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| @Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.and()
.logout()
.permitAll();
}
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("admin").password("admin").roles("USER");
}
}
|
- 除了“/”,”/home”(首页),”/login”(登录),”/logout”(注销),之外,其他路径都需要认证。
- 指定“/login”该路径为登录页面,当未认证的用户尝试访问任何受保护的资源时,都会跳转到“/login”。
- 默认指定“/logout”为注销页面
- 配置一个内存中的用户认证器,使用admin/admin作为用户名和密码,具有USER角色
@EnableWebSecurity
我们自己定义的配置类WebSecurityConfig加上了@EnableWebSecurity注解,同时继承了WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter。你可能会在想谁的作用大一点,毫无疑问@EnableWebSecurity起到决定性的配置作用,它其实是个组合注解。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Import({ WebSecurityConfiguration.class, // <2>
SpringWebMvcImportSelector.class }) // <1>
@EnableGlobalAuthentication // <3>
@Configuration
public @interface EnableWebSecurity {
boolean debug() default false;
}
|
@Import是springboot提供的用于引入外部的配置的注解,可以理解为:@EnableWebSecurity注解激活了@Import注解中包含的配置类。
<1> SpringWebMvcImportSelector的作用是判断当前的环境是否包含springmvc,因为spring security可以在非spring环境下使用,为了避免DispatcherServlet的重复配置,所以使用了这个注解来区分。
<2> WebSecurityConfiguration顾名思义,是用来配置web安全的,下面的小节会详细介绍。
<3> @EnableGlobalAuthentication注解的源码如下:
1
2
3
4
| @Import(AuthenticationConfiguration.class)
@Configuration
public @interface EnableGlobalAuthentication {
}
|
注意点同样在@Import之中,它实际上激活了AuthenticationConfiguration这样的一个配置类,用来配置认证相关的核心类。
也就是说:@EnableWebSecurity完成的工作便是加载了WebSecurityConfiguration,AuthenticationConfiguration这两个核心配置类,也就此将spring security的职责划分为了配置安全信息,配置认证信息两部分。
WebSecurityConfiguration(安全信息配置)
在这个配置类中,有一个非常重要的Bean被注册了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfiguration {
//DEFAULT_FILTER_NAME = "springSecurityFilterChain"
@Bean(name = AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer.DEFAULT_FILTER_NAME)
public Filter springSecurityFilterChain() throws Exception {
...
}
}
|
在未使用springboot之前,大多数人都应该对“springSecurityFilterChain”这个名词不会陌生,他是spring security的核心过滤器,是整个认证的入口。在曾经的XML配置中,想要启用spring security,需要在web.xml中进行如下配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| <!-- Spring Security -->
<filter>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
|
而在springboot集成之后,这样的XML被java配置取代。WebSecurityConfiguration中完成了声明springSecurityFilterChain的作用,并且最终交给DelegatingFilterProxy这个代理类,负责拦截请求(注意DelegatingFilterProxy这个类不是spring security包中的,而是存在于web包中,spring使用了代理模式来实现安全过滤的解耦)。
AuthenticationConfiguration(认证信息配置)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Configuration
@Import(ObjectPostProcessorConfiguration.class)
public class AuthenticationConfiguration {
@Bean
public AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationManagerBuilder(
ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor) {
return new AuthenticationManagerBuilder(objectPostProcessor);
}
public AuthenticationManager getAuthenticationManager() throws Exception {
...
}
}
|
AuthenticationConfiguration的主要任务,便是负责生成全局的身份认证管理者AuthenticationManager。
适配器模式在spring中被广泛的使用,在配置中使用Adapter的好处便是,我们可以选择性的配置想要修改的那一部分配置,而不用覆盖其他不相关的配置。WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter中我们可以选择自己想要修改的内容,来进行重写,而其提供了三个configure重载方法,是我们主要关心的:
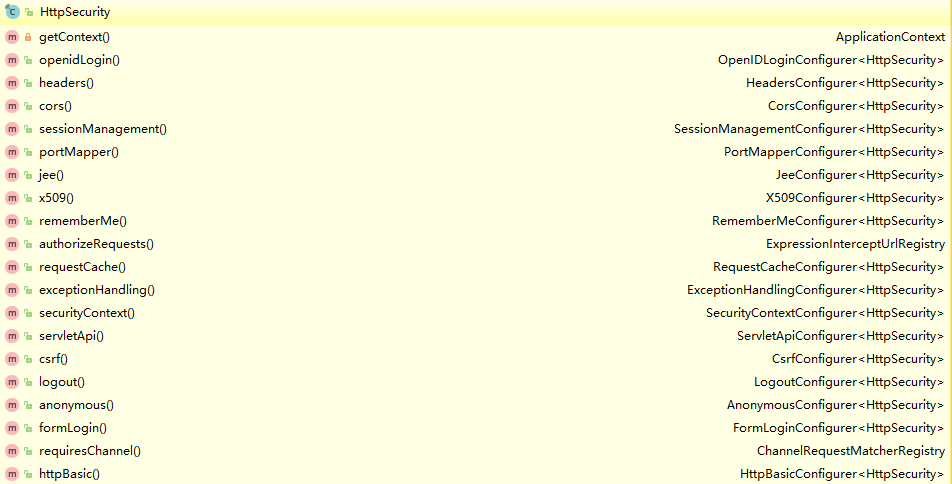
由参数就可以知道,分别是对AuthenticationManagerBuilder,WebSecurity,HttpSecurity进行个性化的配置。
HttpSecurity常用配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| @Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class CustomWebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/resources/**", "/signup", "/about").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/db/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.usernameParameter("username")
.passwordParameter("password")
.failureForwardUrl("/login?error")
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.and()
.logout()
.logoutUrl("/logout")
.logoutSuccessUrl("/index")
.permitAll()
.and()
.httpBasic()
.disable();
}
}
|
上述是一个使用Java Configuration配置HttpSecurity的典型配置,其中http作为根开始配置,每一个and()对应了一个模块的配置(等同于xml配置中的结束标签),并且and()返回了HttpSecurity本身,于是可以连续进行配置。他们配置的含义也非常容易通过变量本身来推测,
- authorizeRequests()配置路径拦截,表明路径访问所对应的权限,角色,认证信息。
- formLogin()对应表单认证相关的配置
- logout()对应了注销相关的配置
- httpBasic()可以配置basic登录
- etc
他们分别代表了http请求相关的安全配置,这些配置项无一例外的返回了Configurer类,而所有的http相关配置可以通过查看HttpSecurity的主要方法得知:
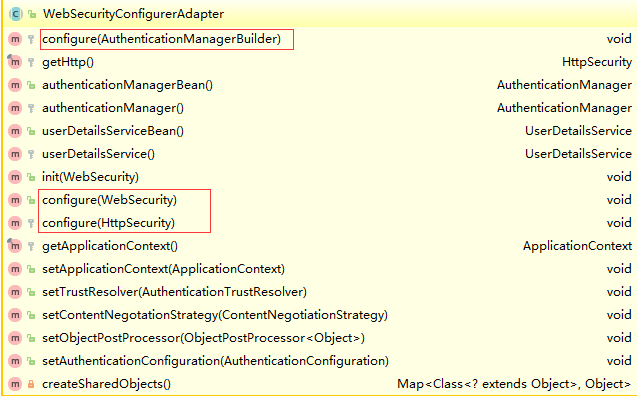
需要对http协议有一定的了解才能完全掌握所有的配置,不过,springboot和spring security的自动配置已经足够使用了。其中每一项Configurer(e.g.FormLoginConfigurer,CsrfConfigurer)都是HttpConfigurer的细化配置项。
WebSecurityBuilder常用配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web
.ignoring()
.antMatchers("/resources/**");
}
}
|
AuthenticationManagerBuilder常用配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("admin").password("admin").roles("USER");
}
}
|
想要在WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter中进行认证相关的配置,可以使用configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)暴露一个AuthenticationManager的建造器:AuthenticationManagerBuilder 。如上所示,我们便完成了内存中用户的配置。
细心的朋友会发现,在前面的文章中我们配置内存中的用户时,似乎不是这么配置的,而是:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("admin").password("admin").roles("USER");
}
}
|
如果你的应用只有唯一一个WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter,那么他们之间的差距可以被忽略,从方法名可以看出两者的区别:使用@Autowired注入的AuthenticationManagerBuilder是全局的身份认证器,作用域可以跨越多个WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter,以及影响到基于Method的安全控制;而 protected configure()的方式则类似于一个匿名内部类,它的作用域局限于一个WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter内部。关于这一点的区别,可以参考我曾经提出的issuespring-security#issues4571。官方文档中,也给出了配置多个WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的场景以及demo,将在该系列的后续文章中解读。
参考资料

