前言
先介绍几个接口,熟悉一下
- Principal: java.security中的接口,用户凭证,其中主要getName()获取用户名
- Authentication:Spring的认证对象接口,继承Principal,包含详细认证信息,常用实现类UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
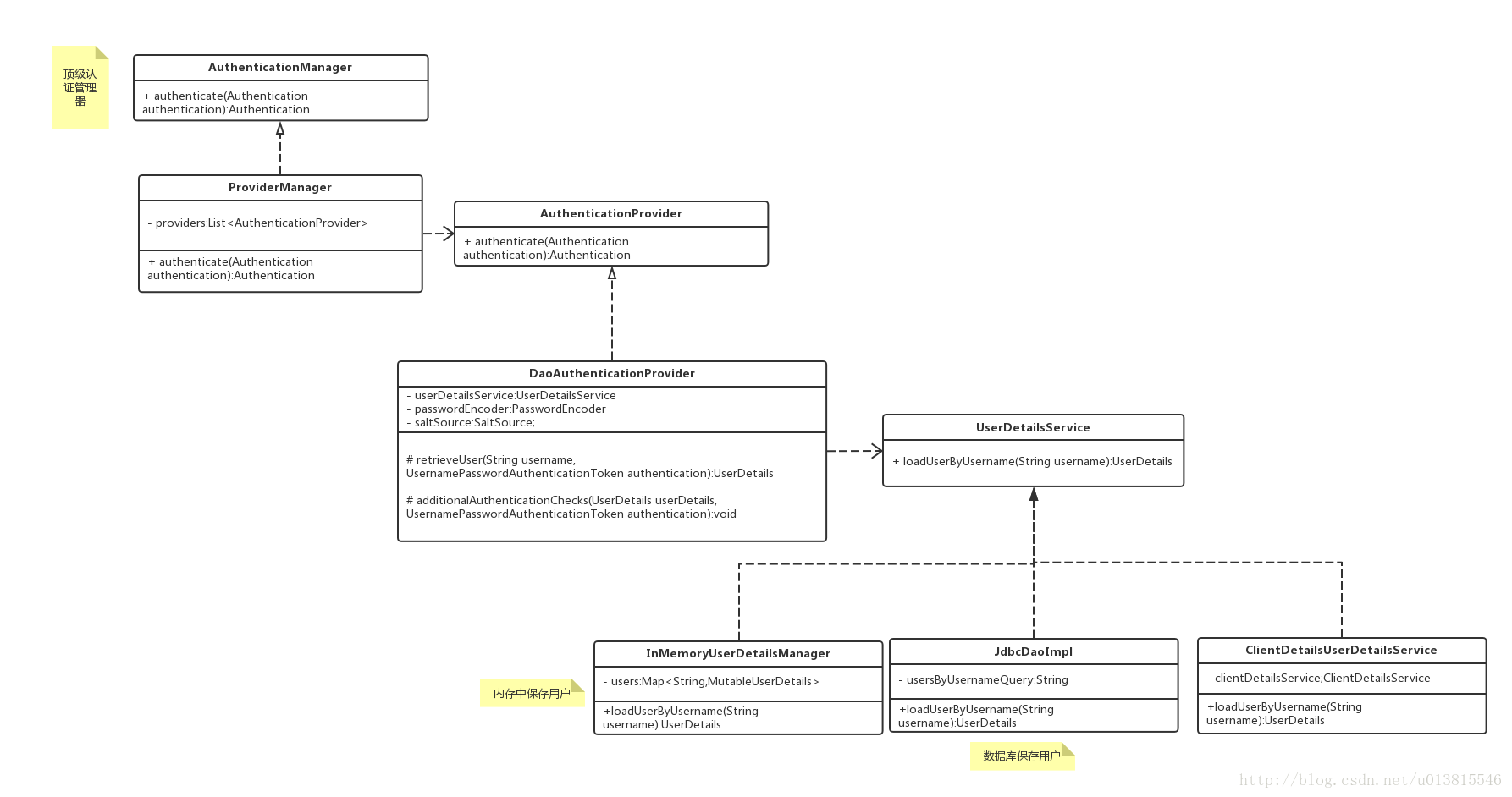
- AuthenticationManager: 认证管理器接口,常用实现类ProviderManager
- ProviderManager: 实现类,包含一个AuthenticationProvider的List
- AuthenticationProvider: 认证提供者接口,提供实际的对Authentication的认证
- DaoAuthenticationProvider: 认证提供者实现类,从db读用户信息,与Authentication进行比对认证
- UserDetails: Spring Security对身份信息封装的一个接口
- UserDetailsService: 从db读用户信息的工具类
入口
- Spring Security的核心入口是一系列的Filter组成的过滤器链
- 经过过滤器链中的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter获取到用户名和密码
- 封装成Authentication,然后进入认证流程
认证流程
认证流程的核心是AuthenticationManager 接口,只有一个authenticate()方法,入参和返回值都是Authentication,但两者确差别很大
- 入参:仅包含了用户名和密码
- 返回值:包含了用户的权限列表、身份信息、详情信息等
所以authenticate()方法核心就是将上面前者转换为后者,且校验密码,之后将认证好的信息设置到安全上下文容器。
在实际需求中,我们可能会允许用户使用用户名+密码登录,同时允许用户使用邮箱+密码,手机号码+密码登录,所以AuthenticationManager一般不直接认证,它内部维护了一个List列表,存放多个AuthenticationProvider,去认证不同的登录方式。在默认策略下,只需要通过一个AuthenticationProvider的认证,即可被认为是登录成功。
按照我们最直观的思路,怎么去认证一个用户呢?用户前台提交了用户名和密码,而数据库中保存了用户名和密码,认证便是负责比对同一个用户名,提交的密码和保存的密码是否相同便是了。AuthenticationProvider最常用的一个实现便是DaoAuthenticationProvider,即校验数据库中的用户名密码。另外内部又用了一个工具类UserDetailsService来,通过用户名加载用户详情,一般情况下,我们只用实现该工具类就可以了。
调用关系如下:
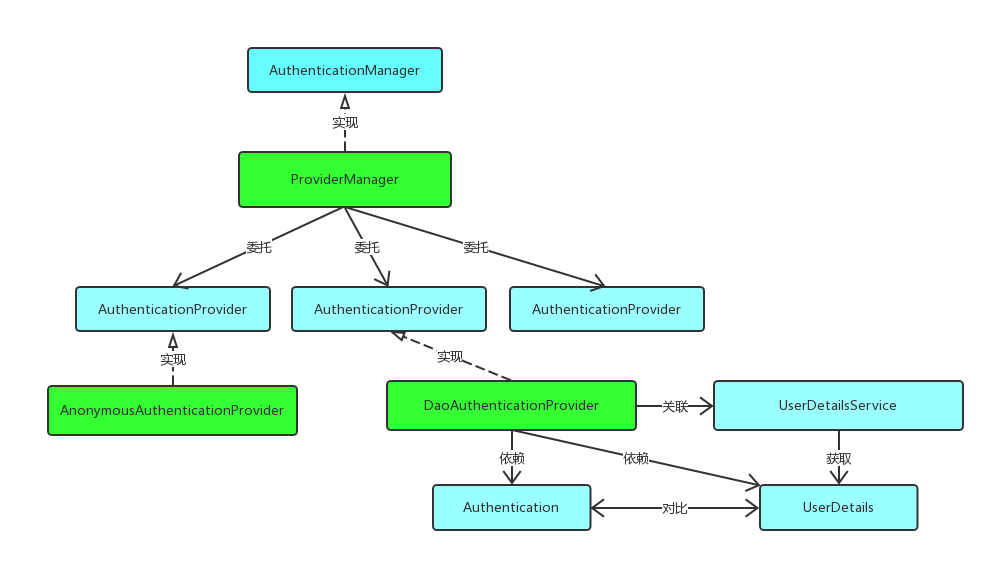
获取当前用户的信息
SecurityContextHolder用于存储安全上下文(security context)的信息。当前操作的用户是谁,该用户是否已经被认证,他拥有哪些角色权限…这些都被保存在SecurityContextHolder中。
SecurityContextHolder默认使用ThreadLocal 策略来存储认证信息。看到ThreadLocal 也就意味着,这是一种与线程绑定的策略。Spring Security在用户登录时自动绑定认证信息到当前线程,在用户退出时,自动清除当前线程的认证信息。
但这一切的前提,是你在web场景下使用Spring Security,而如果是Swing界面,Spring也提供了支持,SecurityContextHolder的策略则需要被替换,鉴于我的初衷是基于web来介绍Spring Security,所以这里以及后续,非web的相关的内容都一笔带过。
因为身份信息是与线程绑定的,所以可以在程序的任何地方使用静态方法获取用户信息。一个典型的获取当前登录用户的姓名的例子如下所示:
1 | Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal(); |
getAuthentication()返回了认证信息,再次getPrincipal()返回了身份信息,UserDetails便是Spring对身份信息封装的一个接口。
Authentication和UserDetails的介绍在下面的小节具体讲解,本节重要的内容是介绍SecurityContextHolder这个容器。
Authentication接口
常用实现类UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)
先看看这个接口的源码长什么样:
1 | public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable { // <1> |
Authentication是spring security包中的接口,直接继承自Principal类,而Principal是位于java.security包中的。可以见得,Authentication在spring security中是最高级别的身份/认证的抽象。
由这个顶级接口,我们可以得到用户拥有的权限信息列表,密码,用户细节信息,用户身份信息,认证信息。如下方法详细解读如下:
- getAuthorities(),权限信息列表,默认是GrantedAuthority接口的一些实现类,通常是代表权限信息的一系列字符串。
- getCredentials(),密码信息,用户输入的密码字符串,在认证过后通常会被移除,用于保障安全。
- getDetails(),细节信息,web应用中的实现接口通常为 WebAuthenticationDetails,它记录了访问者的ip地址和sessionId的值。
- getPrincipal(),敲黑板!!!最重要的身份信息,大部分情况下返回的是UserDetails接口的实现类,也是框架中的常用接口之一。UserDetails接口将会在下面的小节重点介绍。
认证过程example
1 | public class AuthenticationExample { |
AuthenticationManager接口
AuthenticationManager是认证相关的核心接口,常用实现类为ProviderManager
1 | public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager, MessageSourceAware,InitializingBean { |
AuthenticationProvider接口
常用实现类为DaoAuthenticationProvider
AuthenticationProvider最最最常用的一个实现便是DaoAuthenticationProvider。顾名思义,Dao正是数据访问层的缩写,也暗示了这个身份认证器的实现思路。由于本文是一个Overview,姑且只给出其UML类图: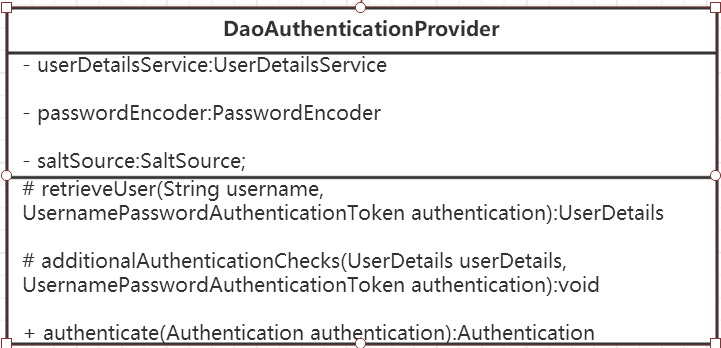
UserDetails与UserDetailsService接口
上面不断提到了UserDetails这个接口,它代表了最详细的用户信息,这个接口涵盖了一些必要的用户信息字段,具体的实现类对它进行了扩展。
它和Authentication接口很类似,比如它们都拥有username,authorities,区分他们也是本文的重点内容之一。Authentication的getCredentials()与UserDetails中的getPassword()需要被区分对待,前者是用户提交的密码凭证,后者是用户正确的密码,认证器其实就是对这两者的比对。Authentication中的getAuthorities()实际是由UserDetails的getAuthorities()传递而形成的。还记得Authentication接口中的getUserDetails()方法吗?其中的UserDetails用户详细信息便是经过了AuthenticationProvider之后被填充的。
UserDetailsService和AuthenticationProvider两者的职责常常被人们搞混,关于他们的问题在文档的FAQ和issues中屡见不鲜。记住一点即可,敲黑板!!!UserDetailsService只负责从特定的地方(通常是数据库)加载用户信息,仅此而已,记住这一点,可以避免走很多弯路。
UserDetailsService常见的实现类有JdbcDaoImpl,InMemoryUserDetailsManager,前者从数据库加载用户,后者从内存中加载用户,也可以自己实现UserDetailsService,通常这更加灵活。